By Lauren Crimp of RNZ
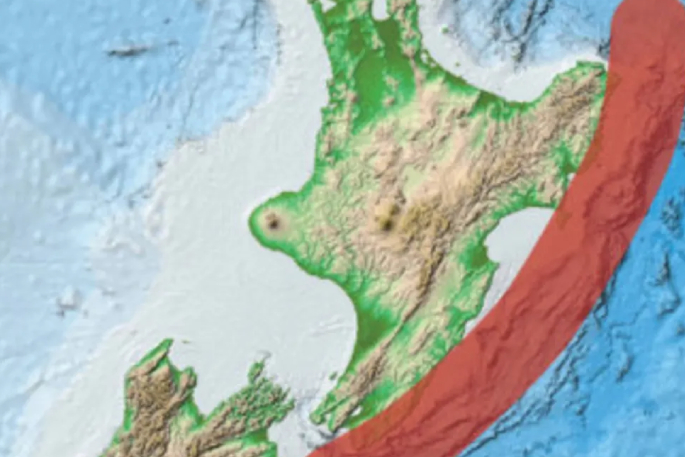
The scale of catastrophe facing Aotearoa in the case of a massive earthquake and tsunami from our largest fault - the Hikurangi subduction zone - has been laid bare by experts.
Tens of thousands of people could die, hundreds of thousands could be displaced, and the cost of building damage could top $100 billion.
Some of the country's top science minds have gathered at Te Papa to discuss the latest disaster risk, resilience and recovery science at a conference run by one of the government-funded National Science Challenges - the Resilience to Nature Challenge.
During a session on catastrophic risk, the National Emergency Management Agency detailed its work over the past 18 months, using a 9.1 Hikurangi earthquake and tsunami as its 'planning scenario'.
"Science tells us that a catastrophic event, such as an alpine fault earthquake, or a Hikurangi fault subduction zone earthquake and tsunami will very likely happen, if not in our lifetime, in our children's," says NEMA chief advisor to the chief executive Sarah Holland.
"It could happen tomorrow."
The fallout
If that level of earthquake hits, there would be four to eight minutes of shaking. For comparison, the ground shook for 10 seconds in the devastating 2011 Canterbury earthquake, Sarah says.
Assuming 70 percent of people were able to evacuate, more than 22,000 would die - mostly in the tsunami - and nearly 26,000 more would be injured.
About 400,000 people would be displaced and 30,000 homes destroyed or damaged from the tsunami alone.
There would be about $144 billion worth of damage to buildings from the earthquake and tsunami.
And the scale of the damage to critical infrastructure is yet to be modelled.
"This class of catastrophic events is beyond our current arrangements, thinking, experience, and beyond our imagination," says Sarah.
But preparation was underway.
The planning
NEMA is planning to respond to "the worst of the worst", working with 50 organisations to create a "catastrophic handbook" which can apply to any disaster, says Sarah.
"That's things like mass casualty management, the provision of food, water and shelter, restorations of critical infrastructure, establishment of emergency supply chains."
International assistance would be vital for the latter, and NEMA was planning for what would be needed, and how it would be distributed upon arrival in New Zealand, she says.
 NEMA chief science advisor Tom Wilson. Photo: Supplied.
NEMA chief science advisor Tom Wilson. Photo: Supplied.
Laying out the potential fallout was scary, but necessary, says NEMA chief science advisor Tom Wilson.
"These are big, big numbers," he says.
"This is what motivated change for chief executives. This is where elected officials really stood up and took notice."
But there was more work to be done in getting government and communities to properly understand the level of risk.
"We will be driven kicking and screaming into that space, by the insurance sector one way or another," he says.
"But we must have a better platform for being able to compare and characterise our risks, and understanding what those potential risk treatments or resilience strategies might be."
Science funding drying up
The science community was urged to keep their work coming.
But that would be tough, with 10-year funding for the National Science Challenges ending in June, says Massey University natural hazards professor Jon Procter.
Some areas of research would have to stop altogether, he says.
"The people doing planning and mitigation will be relying on old knowledge and old scenarios, rather than thinking about the next big thing or the next issue could occur," says Jon.
The National Science Challenges had brought experts together, says University of Canterbury lecturer Kristie-Lee Thomas, who also leads the Challenges' Whanake te Kura i Tawhiti Nui programme which applies mātauranga Māori to natural hazard research.
"Experts across different spaces, mātauranga, science, planning, policy," she says.
"You've built up these really good relationships, these really good teams... we want to continue working together and building up that momentum, but we need the resourcing to keep doing that and keep supporting that planning."
Invest in NEMA - inquiry
Just three weeks before the conference, a national inquiry into last year's weather disasters found Aotearoa was not prepared for large-scale emergencies.
In one of the inquiry's many findings, it noted NEMA is a small organisation that "does not have the funding or expertise to undertake the full breadth of activities it is currently tasked with".
The agency would operate more effectively if it focused on leading readiness and response activities - including setting standards, training, and leading worst-case scenario planning. The inquiry recommended it receive more cash to do so.
Meanwhile, NEMA's own probe into its response to the weather events is due on 16 May.


3 comments
The Master
Posted on 14-05-2024 15:47 | By Ian Stevenson
Obviously the Hauraki EQ zone is of the same nature as in Japan or California, so the answer/s will be the same, not a lot of science required to "study" that over and over....
What really is needed are: -
- The means of residence to get to high ground quickly, as there maybe 10-20 minutes for a Tsunami to arrive.
- Ensure buildings are EQ compliant and built properly to a suitable standard.
- It would obviously be helpful to build on solid ground, e.g. avoid liquefaction zones, wonder if anyone has bothered with that?
- The most at risk areas of the EQ, liquefaction and massive inundation/Tsunami's are Wairapara, HB and the East coast (few people...).
-
Hmmm
Posted on 14-05-2024 17:15 | By Let's get real
I have known of this for years and yet we're only now discussing it openly...?
The fault lines in NZ are reasonably well known and the Hikurangi subduction zone is matched by the Haast fault line, which is also predicted to cause Tsunami and an earthquake of 9+ when that fails.
I have always thought that the "global warming" debate has to be the least significant issue that we should consider. But Queen Jacinda has used this to promote her own self interests extremely well and we now have children worried about our 0.18% emissions and the disaster that we are contributing to.
Don't worry; be happy...
Posted on 15-05-2024 14:23 | By morepork
We don't want to fund scientists who give us bad news, whether it is regarding climate change or natural disaster. The kind of catastrophe being discussed is one we can do little to prevent or mitigate. The best we can do is close the barn after the horse has gone. But we COULD do something about getting better warning and we COULD improve our existing Civil Defence... NEMA should be receiving the funds they need to do an even better job than they do already. For myself, I may have to leave my beloved BOP and look for a property somewhere on the lower slopes of Mt. Taranaki... :-)
Leave a Comment
You must be logged in to make a comment.